In this blog, we explore the pros and cons of mortgage terms. Pick your winner, let the battle of the terms begin.
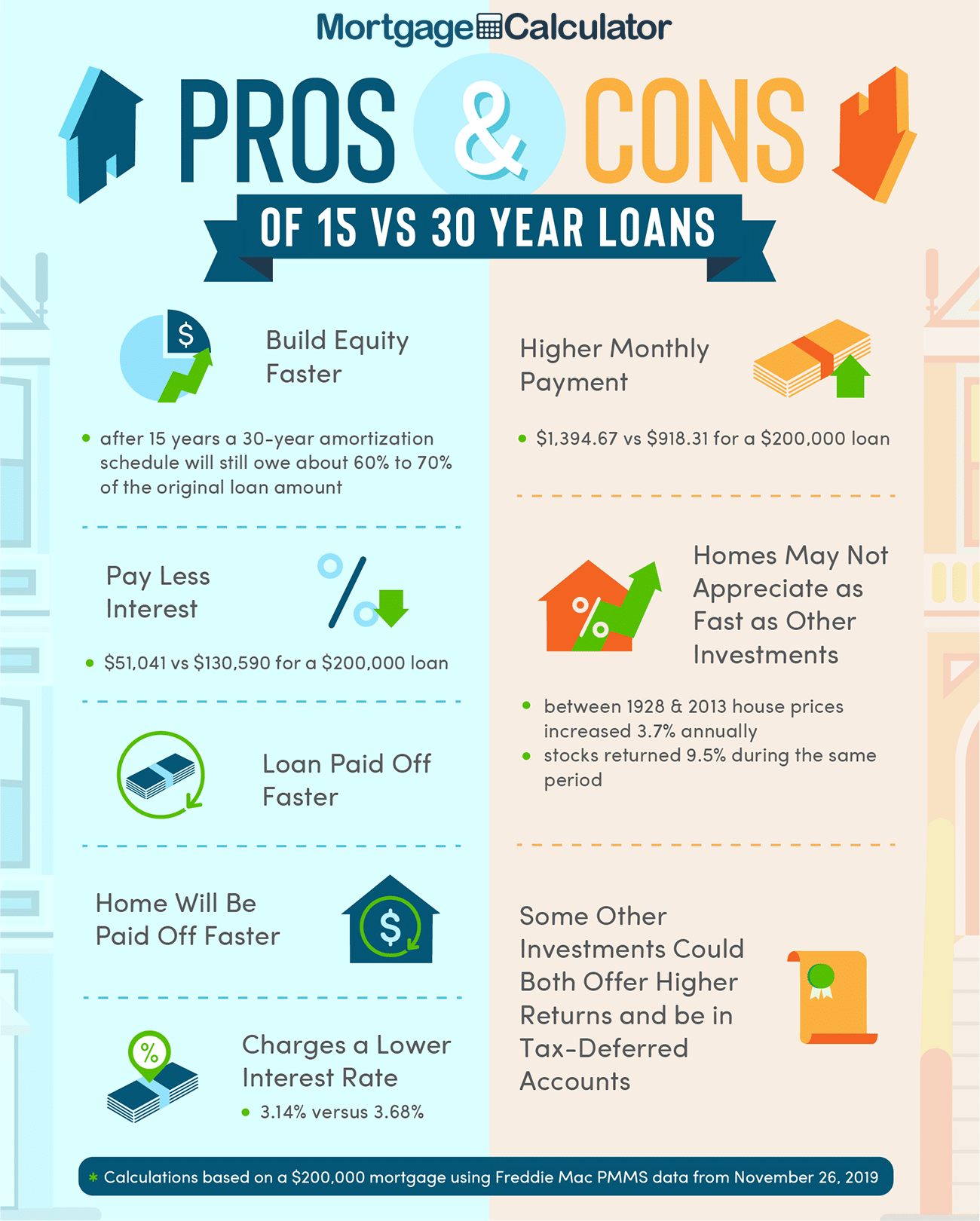
Advantages of a 15-Year Fixed Mortgage:
- Lower interest rate: Typically, 15-year mortgages offer lower interest rates compared to 30-year mortgages. This can result in significant interest savings over the life of the loan.
- Faster equity build-up: With higher monthly payments, you build equity in your home at a faster rate, allowing you to own your home outright sooner.
- Interest savings: Since the loan term is shorter, you pay less interest over the life of the loan.
- Debt-free sooner: With a 15-year mortgage, you can pay off your mortgage faster, allowing you to be debt-free sooner and potentially freeing up your finances for other goals.
Disadvantages of a 15-Year Fixed Mortgage:
- Higher monthly payments: Due to the shorter loan term, the monthly payments for a 15-year mortgage are higher than those for a 30-year mortgage. This can put a strain on your monthly budget.
- Limited flexibility: The higher monthly payments of a 15-year mortgage may limit your financial flexibility. You have less room in your budget for other expenses or investments.
- Less affordable for some borrowers: The higher monthly payments and stricter qualification criteria may make a 15-year mortgage less affordable for some borrowers, especially those with lower incomes or higher debt obligations.
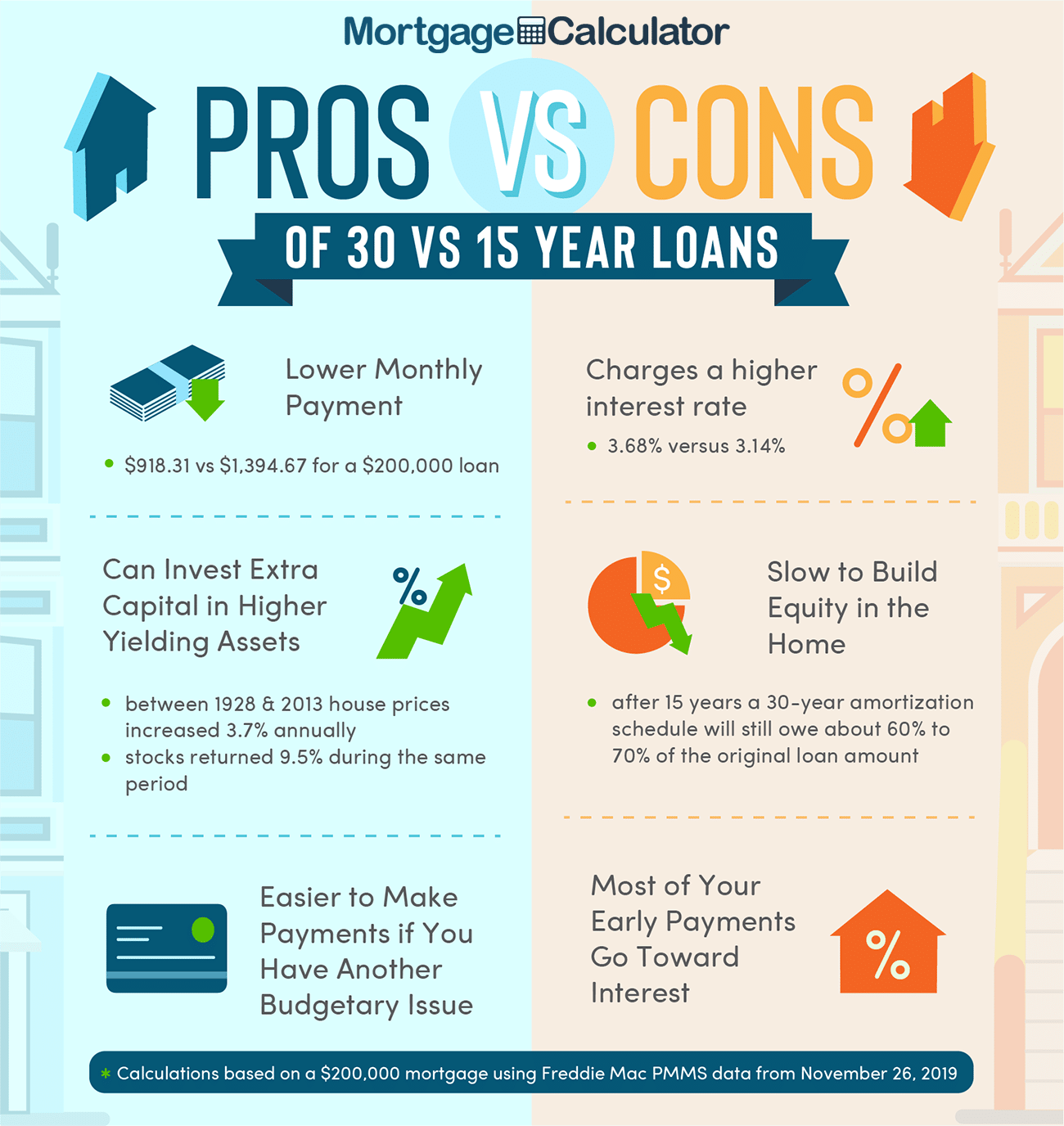
Advantages of a 30-Year Fixed Mortgage:
- Lower monthly payments: The longer loan term of a 30-year mortgage results in lower monthly payments, making it more affordable for many borrowers.
- Greater flexibility: Lower monthly payments provide more financial flexibility, allowing you to allocate funds towards other expenses or investments.
- Easier qualification: The lower monthly payments and more lenient qualification criteria make a 30-year mortgage more accessible to a wider range of borrowers.
Disadvantages of a 30-Year Fixed Mortgage:
- Higher interest costs: Since the loan term is longer, you end up paying more interest over the life of the loan compared to a 15-year mortgage.
- Slower equity build-up: With lower monthly payments, the rate at which you build equity in your home is slower compared to a 15-year mortgage.
- Higher interest rate: Typically, 30-year mortgages have higher interest rates compared to 15-year mortgages, resulting in higher overall interest costs.
Bottomline, the choice between a 15-year and 30-year mortgage depends on your financial situation, long-term goals, and risk tolerance. If you can comfortably afford the higher monthly payments and prioritize paying off your mortgage quickly, a 15-year mortgage may be advantageous. However, if you prefer lower monthly payments and greater financial flexibility, a 30-year mortgage may be more suitable. It’s essential to carefully consider your financial goals and consult with a mortgage professional to make an informed decision.